Delivery of quality healthcare is becoming more complex. Demands for efficiency, maintaining costs, and continuously improving patient care remain an ongoing challenge.
Delivery of quality healthcare is becoming more complex. Demands for efficiency, maintaining costs, and continuously improving patient care remain an ongoing challenge. An ageing population, the need to expand geographic reach, healthcare provider shortages and unprecedented cost pressures are stretching the resources of healthcare providers like never before. Addressing many of these challenges is the use of real time video, and wireless telephony solutions.
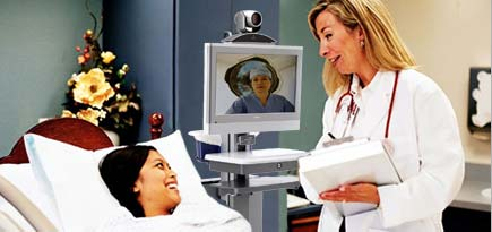
Telehealth- Bridging the Gap to Healthcare
Telehealth is emerging as a key trend in the telemedicine sector. Recent advances, notably the emergence of High Definition (HD) technology, have evolved telehealth to a level where it not only provides a high level of clinical efficacy, but also satisfies the assessment and modality requirements of healthcare professionals. Real-time HD images allow the most life-like interactions between clinicians and patients regardless of where either is located. With healthcare provider shortages; mal distribution of specialist in urban areas; an aging population and soaring costs, telemedicine promises to play a key role in addressing the equity of care and cost issues which are brought on by geographic location. HD video solutions are interoperable with all standards based medical peripheral devices. A clinician can’t only see and hear a patient from a distance, but they can also use a digital electronic stethoscope to listen to their heart and lung sounds, use an electronic otoscope to look into their ear or use a general exam camera to view skin lesions. The use of telemedicine as quality way of providing patient care is increasingly being backed by data and the development of standards.
Distant Medical Education- Knowledge Anywhere at Anytime
The body of knowledge of medicine is increasing at an exponential rate. The US National Institute of Health has anticipated that some medical specialties to double their knowledge base within the next 4-6 years. A major barrier and challenge is the distribution of this knowledge from medical centers of excellence to healthcare professionals regardless of where they’re located. Unified Collaboration and the advancements in HD video, streaming and archiving are breaking down the barriers to when and where medical education can be provided. With the ability to share HD video, Voice, and content in real time or through archived streaming video anywhere in world, clinicians can experience the most life like experience without leaving their home, desk, boardroom or education center. Many countries, states and or provinces mandate that healthcare professionals receive a certain number of continuing medical education hours each year to maintain their skills and maintain their license practice medicine.

Healthcare Administration- Increased Efficiency
Whether private, government or not for profit, it’s imperative that healthcare organizations run their day-to-day business as efficiently as possible. Large geographic distances, high fuel costs, lost of productivity while driving and air travel all lead to increased use of Telepresence solutions for general meetings, project development, board meetings, budget reviews and vendor relations. Once study conducted in the United States (Maine) showed that by simply utilizing telepresence video solutions instead of driving for a one, two-hour meeting that occurred once every two weeks, they saved $14,130 USD over the course of a year. Healthcare organizations are enterprises and day-to-day communication in an efficient manner helps the bottom line.
The realization that telepresence solutions can allow project development between geographically dispersed organizations in a timely and efficient manner that was not previously achievable. The use of real time telepresence for social service applications is increasing dramatically. Statues in many countries mandate appropriate communication for both sign language interpreting and spoken language. One example, the Americans’ with Disabilities Act (ADA) mandates that appropriate communication is provided by healthcare organizations for the Deaf and Hard of Hearing. There are also legal risks for hospitals and healthcare providers if proper communication can’t take place for obvious reasons. Shortages of certified medical interpreters and large travel distances make it difficult and extremely expensive to have certified interpreters. Telepresence video solutions are effectively being used to increase access to interpreter services with significant cost savings.
Wireless Telephony – Enabling Mobile Healthcare Workers
Few people realize that the healthcare industry led the way in implementing wireless voice communications and have been deploying wireless telephones systems for more than 15 years. With a true need for worker mobility, hospitals were the earliest adopters of this technology. In fact, few industries have a more mobile work force. And with nursing shortages and high patient-to-nurse rations, the need for real-time communications and accessibility has never been greater.
Wireless telephones provide hospital workers immediate access to each other and, most importantly, to patients, resulting in higher patient satisfaction. With wireless phones, nurses don’t miss calls or waste time traveling between the nurse station and patient rooms. Physicians can contact nurses directly for orders and, if a nurse is busy, calls can be rerouted. Other departments benefit as well; emergency personnel can stay with a patient through the triage process and do not spend time searching for staff or information, and radiologists, pharmacists, technicians and transporters can be contacted directly with a hospital-wide implementation thereby eliminating paging delays.
Most wireless telephones connect to the hospital’s telephony system, allowing them to emulate traditional desk phones. In a way, it’s like having a cellular telephone for work — one without the coverage, airtime and power-emission issues inherent with cell phones.
In addition to improving real-time voice communications, many of today’s wireless telephone systems integrate with to other applications, allowing for text messaging – examples include patient care and business systems such as nurse call, voice recognition, telemetry, patient monitoring, alarms, and real-time location tracking. Patients can reach their assigned nurse directly from their bedsides, and an alert can be sent to a nurse if a problem is detected while monitoring a patient. For example, a nurse can give a patient his or her extension so that patient can reach the nurse directly.
At hospitals where wireless communications are used, patients are reassured knowing they have immediate access to an assigned nurse. Another added benefit is that wireless telephones help eliminate the need for overhead paging, which can be disruptive, inefficient and indiscreet. A quieter environment seems to accommodate better patient healing and satisfaction.
By integrating wireless telephones with these systems, hospitals streamline their communications structure — cutting response times, improving information flow between patients and caregivers, lowering noise levels, and as a result, improving overall patient care. And ultimately, improving job satisfaction for overworked, under-resourced healthcare providers.
Clearly, time saved impacts the bottom line. And in an industry where it’s not just business — it’s lives at stake — the bottom line is critical.
Summary – Adapting to Changing Healthcare Requirements
Like many industries, the one constant in the evolving world of healthcare is change. Interactive communications tools like real-time video, tele presence and wireless telephony solutions are addressing significant real-world challenges that impact healthcare organizations today and will continue to adapt to help address the challenges we will face tomorrow.

















